Hello, you are using an old browser that's unsafe and no longer supported. Please consider updating your browser to a newer version, or downloading a modern browser.
Hello, you are using an old browser that's unsafe and no longer supported. Please consider updating your browser to a newer version, or downloading a modern browser.
Published by Mike McNelis on June 7, 2024

In recent years, cyber threats have become more sophisticated, and traditional security measures have often fallen short. The Zero Trust Security Model is an emerging approach designed to address these challenges by verifying every user and device.
At Training Camp, we believe in proactive security measures that adapt to modern threats. This post explores the essential aspects of Zero Trust, its benefits, and strategies for implementation.
Understanding the Zero Trust Security Model involves a deep dive into its definition, core principles, and key components that differentiate it from traditional security models.
Zero Trust is a security model based on the principle of never trusting and always verifying. Unlike traditional models that often give implicit trust to users inside the network, Zero Trust continuously verifies every user and device trying to access resources. Explicit verification and least-privilege access are core principles. This means only providing the minimum required access to perform a task, significantly reducing the attack surface.
Traditional security models often focus on perimeter defense, assuming everything inside the network is trusted. However, 34% of data breaches originate from internal network users. Zero Trust shifts this paradigm by assuming that threats could be internal and external. It doesn’t rely on network location for access, making it more suitable for today’s remote and hybrid work environments. Continuous verification, even after initial authentication, is crucial in Zero Trust, unlike traditional models that may only check once.
Key components of Zero Trust include identity and access management, endpoint security, and data protection. Tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA) play a significant role. According to Microsoft, using MFA can block 99.9% of account compromise attacks. Micro-segmentation of networks, another key component, limits lateral movement by dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments.

Adopting Zero Trust involves several technologies and strategies, such as strong encryption of data in transit and at rest, continuous monitoring, and automated threat responses. Microsoft offers robust solutions to help organizations implement these technologies effectively.
For a deeper understanding of the technologies involved, exploring security automation trends can provide valuable insights.
Enhanced protection against cyber threats is one of the major advantages of adopting a Zero Trust Security Model. This approach has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of breaches, providing a robust defense against both internal and external threats. By continuously verifying every access request and enforcing least-privilege access, organizations can minimize their attack surface and reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access. A report by Microsoft highlights that implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can prevent up to 99.9% of attacks targeting account credentials, a staple practice in Zero Trust.
Compliance with regulatory standards is easier with Zero Trust. Organizations must adhere to strict data privacy laws and industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. The continuous verification and granular access controls in Zero Trust facilitate better compliance management. For instance, capabilities for detailed logging and auditing enable organizations to track access and data usage comprehensively. This can simplify the process of demonstrating compliance during audits. Furthermore, automated compliance reporting tools integrated within Zero Trust solutions can save significant time and resources, ensuring that compliance mandates are consistently met.
Zero Trust enhances network visibility and control by continuously monitoring traffic and activities across the network. Traditional models often lack the granularity needed to detect and respond to sophisticated threats, but Zero Trust’s constant verification approach fills this gap. Tools for real-time monitoring and advanced analytics provide insights into user behavior and data flows. For example, micro-segmentation helps in isolating network segments, preventing lateral movement by attackers within a compromised segment. According to a study by the Cloud Security Alliance, this isolation technique is crucial in mitigating breach impact. For more insights on network protection strategies, key strategies for defending networks offers practical advice.

By adopting Zero Trust, organizations not only strengthen their cybersecurity posture but also gain a competitive edge through improved regulatory compliance and enhanced operational efficiency. Zero Trust isn’t just a trend; it’s a transformational approach to modern security challenges.
Next, we’ll discuss practical steps to implement a Zero Trust strategy in your organization.
Implementing the Zero Trust Security Model requires a structured approach that emphasizes assessment, layered security, and continuous adaptation. Let’s look at these key aspects to help your organization transition to this robust security framework.
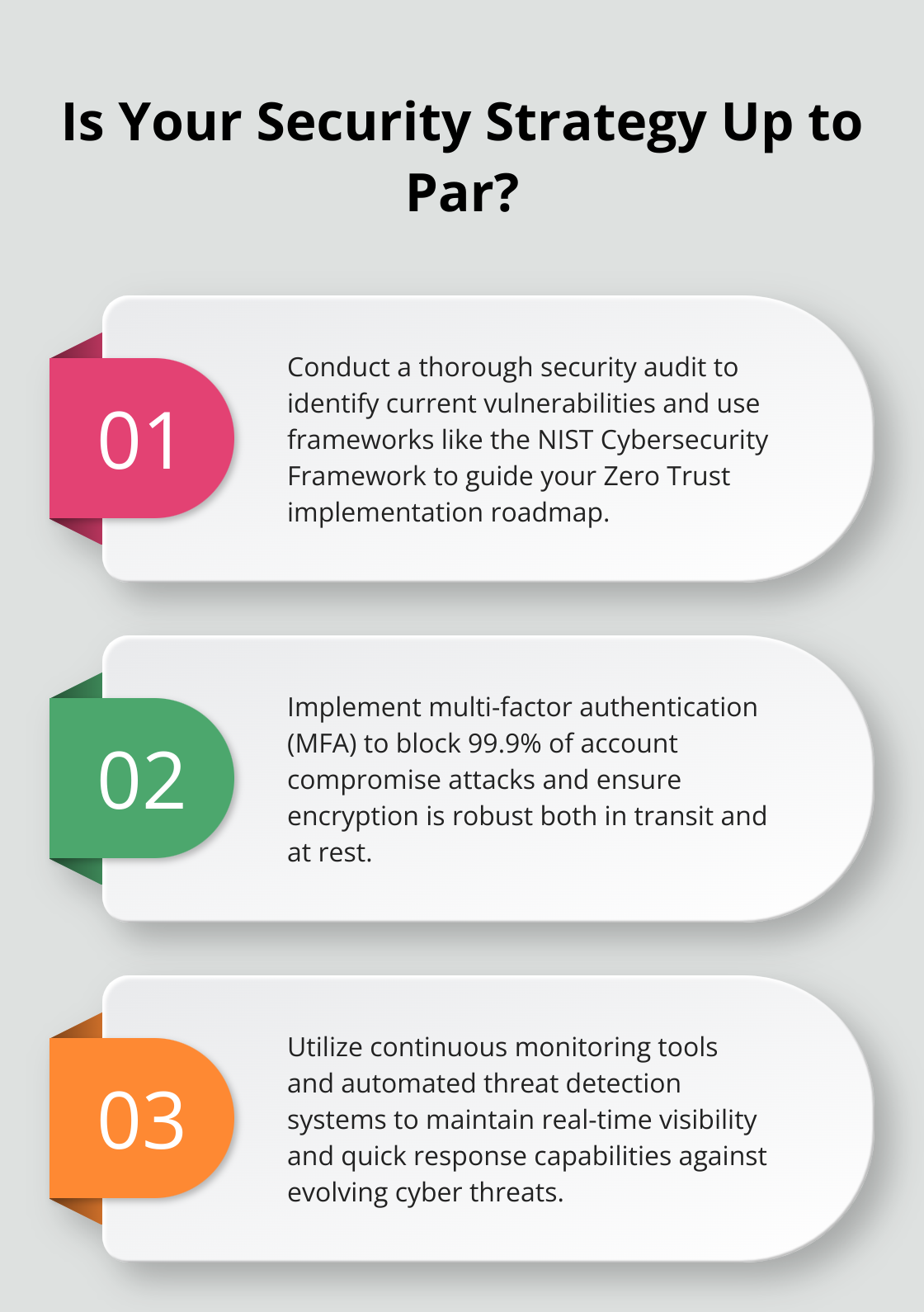
Before adopting Zero Trust, conduct a thorough evaluation of your existing security measures. Start by identifying weaknesses and vulnerabilities in your network. Assess how data, identity, and access controls are managed. A detailed security audit will reveal gaps in your current defenses and highlight areas for improvement.

Organizations often use security frameworks such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework to benchmark their posture. These standards offer a baseline for evaluating current practices against best practices. Data from your audits can guide the implementation roadmap, ensuring that critical vulnerabilities are addressed first.
Zero Trust is not a single product but a multi-layered strategy. Start by implementing strong identity and access management solutions, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA). Given that MFA can block 99.9% of account compromise attacks, its integration is non-negotiable.
Next, secure all endpoints. Advanced endpoint protection and encryption create another security layer to protect data. Ensure that sensitive data is encrypted, both in transit and at rest. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools can provide real-time threat detection and incident response capabilities.
Micro-segmentation should be another priority. By dividing your network into smaller segments, each isolated from the other, you minimize the potential for lateral movement by attackers. Micro-segmentation has been proven to be a critical control, reducing attack surfaces within a network.
Zero Trust requires continuous verification and real-time monitoring of all network activities. Implement tools that provide visibility into user behavior and data flows. Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to collect and analyze security data continuously. These systems can identify abnormal activities and trigger automated responses.
Automated threat detection and response systems are essential. They enable quicker containment of threats and reduce the time attackers have within your environment. According to a study, automated threat response can reduce containment times by up to 50%.
Regularly update and adapt your Zero Trust strategies based on new threat landscapes. Cyber threats evolve, and so should your defenses. Periodic reviews and updates to your security policies and procedures are crucial for maintaining an effective Zero Trust posture. For additional tips on adapting to new security landscapes, explore our insights on security analytics.
By meticulously assessing your current security, adopting a multi-layered approach, and ensuring continuous monitoring, your organization can significantly enhance its defenses against both internal and external threats.
Zero Trust offers a transformative approach to cybersecurity by fundamentally redefining how access and security measures are enforced. It emphasizes continuous verification, least-privilege access, and the assumption that threats can come from both within and outside the network. These principles help mitigate the risks associated with internal data breaches, which account for 34% of such incidents. By integrating key technologies like multi-factor authentication and micro-segmentation, organizations can enhance their ability to protect sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance.
In the modern security landscape, Zero Trust is indispensable. Its continuous monitoring and real-time threat detection capabilities provide a robust defense against advanced cyber threats. The model’s ability to adapt to remote and hybrid work environments makes it particularly relevant today. With 76% of large organizations already adopting Zero Trust, it is clear that this approach is becoming the standard for effective cybersecurity.
Moving forward with Zero Trust involves a clear-eyed assessment of your current security posture, adopting a multi-layered defense strategy, and ensuring continuous adaptation to evolving threats. Organizations can benefit from established frameworks like NIST to guide their implementation processes. The integration of automated systems for threat detection and response will be crucial in achieving faster containment and minimizing the attack window.
For those looking to implement and master Zero Trust security, we at Training Camp offer tailored training programs designed to help professionals acquire the necessary skills and certifications. Our award-winning IT certification programs, including live, online, and boot camp courses, come with an Exam Pass Guarantee. Whether you’re preparing for certifications like CompTIA Security+ or looking to enhance your compliance training, explore our training options to empower your cybersecurity efforts. For additional resources on effective approaches to network protection, check our insights on defending networks.
Adopting Zero Trust is not just about following a trend; it is about building a resilient security framework that can adapt and evolve with the times. With the right training and continuous commitment to security best practices, you can secure your organization against the complexities of modern cyber threats.
Back to All Posts